What is the purpose of pickling seamless steel pipes?
Pickling and passivation of seamless steel pipes is a chemical reaction. First, the oxide scale and rust on the steel surface can be removed through the pickling solution, and the passivation process is completed at the same time. It can effectively prevent the oxidation of seamless steel pipes and achieve the purpose of anti-corrosion. Before pickling and passivating seamless steel pipes, oil, degreasing, and surface drawing compounds and other impurities must be removed. The surface of the seamless steel pipe after pickling and passivation turns into a uniform silvery white color, which greatly improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel.

Phosphating of seamless steel pipes is a process in which seamless steel pipes are immersed in a phosphating solution (a solution based on some acid phosphates) and deposited on the surface to form a layer of water-insoluble crystalline phosphate conversion film. Phosphating is A process in which chemical and electrochemical reactions form a phosphate chemical conversion film. The formed phosphate conversion film is called a phosphating film, which prevents metal from being corroded to a certain extent; it is used as a primer before painting to improve the paint quality. The adhesion and anti-corrosion ability of the film layer; used for friction reduction and lubrication in the metal cold working process.
The "phosphating and saponification" of seamless steel pipes refers to a process of re-saponification after phosphating. It is generally used in machining processes such as drawing or stretching. After the phosphating film is generally 8-12 microns, it enters the saponification solution and is then pulled or stretched. The purpose of saponification of seamless steel pipes is to further increase the lubrication performance.
The brief process of pickling, phosphating and saponifying seamless steel pipe operating procedures: pickling → high pressure washing → phosphating → high pressure water washing → saponification → drying → transportation and stacking.
Pickling of seamless steel pipes
1. Pickling definition: Acids use chemical methods to remove iron oxide scale according to a certain concentration, temperature, and speed, which is called pickling.
2. Pickling classification: According to the type of acid: sulfuric acid pickling, hydrochloric acid pickling, nitric acid pickling, and hydrofluoric acid pickling. Pickling must use different media according to the material of the steel, such as pickling carbon steel with sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, pickling stainless steel with a mixed acid of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, etc. According to the shape of the steel, it is divided into: wire rod pickling, forging pickling, steel plate pickling, strip pickling, etc. According to the type of pickling equipment: tank pickling, semi-continuous pickling, fully continuous pickling, and tower pickling.
3. Principle of pickling: Pickling is a process of removing iron oxide scale from the metal surface using chemical methods, so it is also called chemical pickling. The iron oxide scale (Fe203, Fe304, Fe0) formed on the surface of the steel pipe is an alkaline oxide that is insoluble in water. When they are soaked in an acid solution or an acid solution is sprayed on the surface, these alkaline oxides can A series of chemical changes occur with acids.
Because the iron oxide scale on the surface of carbon structural steel or low alloy steel is loose, porous and cracked, and the iron oxide scale is straightened, stretched and conveyed along with the strip in the pickling unit, it is repeatedly bent. The pores and cracks further increase and expand, so while the acid solution reacts chemically with the iron oxide scale, it also reacts with the matrix iron of the steel through the cracks and pores.
In other words, at the beginning of pickling, chemical reactions between three kinds of iron oxide scale, metallic iron and acid solution are going on at the same time.
⑴ Iron oxide scale reacts chemically with acid and is dissolved (dissolution).
⑵ Metal iron reacts with acid to generate hydrogen gas, which mechanically peels off the iron oxide scale (mechanical peeling effect).
⑶ The generated atomic hydrogen reduces the iron oxide to ferrous oxide which is easy to react with acid, and then reacts with acid to be removed (reduction).
Passivation of seamless steel pipes
1. Passivation principle: The passivation mechanism can be explained by the thin film theory, that is, passivation is due to the interaction between metal and oxidizing substances, which generates a very thin, dense, and good covering property on the metal surface. Passivation film firmly adsorbed on the metal surface. This film exists as an independent phase, usually a compound of oxidized metals. It plays the role of completely separating the metal from the corrosive medium, preventing the metal from contacting the corrosive medium, so that the metal basically stops dissolving and forms a passive state to prevent corrosion.
2. Advantages of passivation:
1) Compared with the traditional physical sealing method, passivation treatment has the characteristics of absolutely not increasing the thickness of the workpiece and changing the color, improving the precision and added value of the product, making the operation more convenient;
2) Since the passivation process is carried out in a non-reactive state, the passivation agent can be added and used repeatedly, so the life is longer and the cost is more economical.
3) Passivation promotes the formation of an oxygen molecular structure passivation film on the metal surface. The film layer is dense and stable in performance, and it also has a self-repairing effect in the air. Therefore, compared with the traditional method of applying anti-rust oil, the passivation formed by passivation Passivation film is more stable and corrosion resistant.
Most of the charge effects in the oxide layer are directly or indirectly related to the thermal oxidation process.
In the temperature range of 800→1250°C, the thermal oxidation process using dry oxygen, wet oxygen or water vapor has three continuous stages. First, oxygen in the ambient atmosphere enters the generated oxide layer, and then the oxygen passes through the oxygen dioxide layer. Silicon diffuses internally, and when it reaches the Si02-Si interface, it reacts with silicon to form new silicon dioxide.
In this way, the entry-diffusion-reaction process of oxygen continues to occur, so that the silicon near the interface is continuously converted into silicon dioxide, and the oxide layer grows into the inside of the silicon wafer at a certain rate.
Phosphating of seamless steel pipes
Phosphating treatment is a surface treatment process that forms a film (phosphating film) on the surface through a chemical reaction.
The phosphating treatment process is mainly used on metal surfaces. The purpose is to provide a protective film on the metal surface to isolate the metal from the air and prevent it from being corroded. It is also used as a primer before painting some products. With this layer of phosphorus The chemical film can improve the adhesion and anti-corrosion ability of the paint layer, improve the decoration and make the metal surface look more beautiful, and can also play a lubrication role in the cold working process of some metals.
After phosphating treatment, the workpiece will not be oxidized and rusted for a long time. Therefore, phosphating treatment is widely used and is also a commonly used metal surface treatment process. It is used more and more in industries such as automobiles, ships, and machinery manufacturing. Come more and more.
1. Classification and application of phosphating
Normally, a surface treatment will show one color, but phosphating treatment can show different colors according to actual needs by using different phosphating agents. This is why we often see phosphating. The treatment is available in gray, color or black.
Iron-based phosphating: After phosphating, the surface will show rainbow colors and blue, so it is also called colorful phosphorus. The phosphating solution mainly uses molybdate as raw material, and will form a rainbow-colored phosphating film on the surface of steel materials. It is also mainly used for coating the bottom layer to achieve the anti-corrosion ability of the workpiece and improve the adhesion of the surface coating.
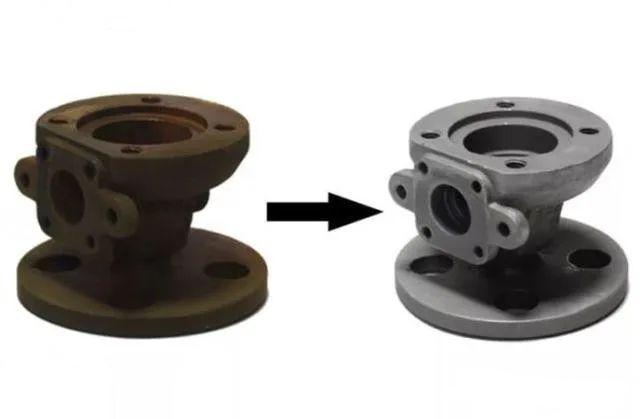


2. Pickling and passivation seamless steel pipe process flow
Seamless steel pipe pickling and passivation The secondary cold drawing of seamless steel pipe is raw material (capillary tube or finished pipe)→heading→pickling→phosphorus saponification (i.e. lubrication)→cold drawing. If there is a second cold drawing, does it need to be annealed? It depends on what kind of steel it is.
Generally, low carbon steel does not need to be annealed. After cold drawing → lubrication → cold drawing → annealing → straightening → cutting → finished product inspection → packaging and storage. Finally, if the quality requirements are high, pickling and passivation treatment is performed.
The conventional process of pickling and passivating treatment of seamless pipes. In order to ensure the quality of pickling and passivating, the method of pickling and passivating must first be considered by soaking in pickling passivation liquid. Only when it is inconvenient to soak in liquid can be used. Consider using the method of applying pickling passivation paste, but it is not appropriate to apply the method of applying pickling passivation liquid. When using the method of soaking in pickling passivation solution, the soaking solution needs to be tested and assayed regularly. The conventional process of pickling and passivating steel pipes is as follows: → Pickling → Rinse → Passivation (pool washing) → Pretreatment → → Acid Washing and passivating (two-in-one) liquid (pool washing) → Rinse → Post-treatment → Pickling and passivating (two-in-one) paste (pool washing) → 5.1 Pretreatment 5.1.1 Remove spatter and splash on the surface of the weld and base metal. Welding flux, dust, etc.
3. The role of pickling and passivating seamless steel pipes
During the process of prefabrication, welding, testing and heat treatment, iron oxide, welding slag, grease and other dirt will accumulate on the surface of the pipe (carbon copper pipe, stainless steel pipe), causing the corrosion resistance of the pipe to change. After the pipe is cleaned with pickling liquid, the dirt on the surface of the pipe can be removed; and then through passivation treatment, a protective film against oxidation can be formed on the surface of the steel pipe, so that the corrosion resistance of the steel pipe becomes better and the production process is ensured. normal operation.
4. Pay attention to the pickling and passivation of seamless steel pipes. It is necessary to pay special attention to the following points when pickling:
(1) Seamless steel pipes cannot be pickled with highly corrosive formulas, otherwise local corrosion will occur. However, austenitic stainless steel can be pickled using the process of pickling stainless steel.
(2) The formula containing chloride ions has a faster pickling speed and is only used for the initial pickling of thick oxide films. After the initial pickling, other pickling processes are used for the second pickling. Chloride ions can easily cause pitting corrosion of stainless steel. When preparing the pickling solution, try to use distilled water to prevent the mixing of chloride ions.
(3) When scrubbing, rolling, or pickling with pickling paste, the pickling surface should always be kept moist and cannot be dried. Otherwise, the local acid concentration will be too high, which will produce cloudy patterns.
(4) During various pickling processes, attention must be paid to strictly controlling process conditions such as pickling temperature and time. Otherwise, insufficient pickling, over-pickling, and even workpiece corrosion and scrapping may occur.
There are many production and technological processes for seamless steel pipes, and they are also relatively complex. Pickling and passivation are used in the production of seamless steel pipes. The purpose of this is to add a protective film to the seamless steel pipes. Seamless steel pipes are made stronger and more durable, making their advantages more prominent. So what issues should be paid attention to during the pickling process of seamless steel pipes? What are the advantages?
5. Features and advantages of pickling products:
1: Carbon steel pickling and passivating solution combines pickling and passivation into one, greatly improving labor productivity.
2: The use and operation of the pickling passivation solution is very convenient. Use small and medium-sized carbon steel pipe fittings for tank washing and soaking, or operate by brushing or spraying, and rinse with clean water.
3: The use temperature is 5-30 degrees Celsius, and the pickling and passivation takes about 5-15 minutes to achieve the pickling effect.
4: Seamless steel pipe passivation, sometimes also called "pickling". If the corrosion products generated by the metal due to the action of the medium have a dense structure and form a thin film (often invisible) that tightly covers the surface of the metal, it will change the surface state of the metal and make the electrode potential of the metal greatly increase. Jump in the positive direction and become a corrosion-resistant passive state. For example, when Fe→Fe++, the standard potential is -0.44V. After passivation, it jumps to +0.5~1V, showing corrosion-resistant noble metal properties. This thin film is called a passivation film. The passivation of metal may also be a spontaneous process. (For example, a layer of insoluble compounds is formed on the surface of the metal, that is, an oxide film). In industry, passivating agents (mainly oxidants) are used to passivate metals to form a protective film.
Why do ordinary seamless steel pipes need to be pickled? Hot-rolled pipe materials or in-process pipes after intermediate heat treatment. Before cold processing of ordinary seamless pipes, the oxide scale on the inner and outer surfaces should be removed. The existence of iron oxide scale, on the one hand, affects the quality of subsequent lubrication; on the other hand, because its hardness is higher than the base metal, it will be pressed into the surface of the seamless steel pipe during cold working, causing defects. The result is: friction increases during processing deformation, tool wear intensifies, and the surface quality of the seamless steel pipe decreases, making the cold working process unable to proceed normally and effectively.
Therefore, it is very important to remove the oxide scale on the surface of the pipe material and the product. In the cold processing production of seamless steel pipes, chemical methods are widely used to remove iron oxide scale, that is, pickling is generally used for carbon steel seamless pipes and low-alloy seamless steel pipes, and pickling or alkali is used for high-alloy seamless steel pipes. Acid compound cleaning method.
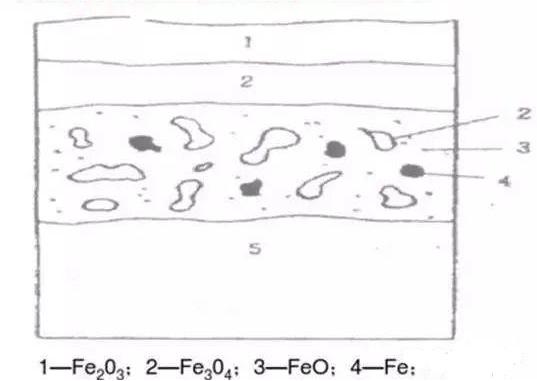
The iron oxide scale on the surface of ordinary carbon steel seamless steel pipes is mainly composed of three iron oxides: iron dioxide (Fe2O3), ferric oxide (Fe3O4) and ferrous oxide (FeO). In the part of the iron oxide scale close to the air, there are more oxygen atoms, so Fe2O3 with more oxygen is generated (oxygen accounts for 30% of it), and Fe2O3 with medium oxygen content is generated in the middle part (of which oxygen content is 27.6%) , and in the part closest to the iron matrix, FeO with low oxygen content is generated (the oxygen content accounts for 22.2%).
Generally, the structure of iron oxide scale generated by ordinary seamless steel pipes at temperatures greater than 575°C is divided into three layers: the first layer is Fe2O3; the second layer is Fe3O4; and the third layer is a mixture of Fe3O4 and FeO. The third layer, the thickest, accounts for about 80% to 85% of the iron oxide scale thickness; the second layer, accounts for about 4% to 18%; the first layer, the thinnest, only accounts for 1% to 2%. However, the thickness of the iron oxide scale and the proportion of each layer are not fixed, but vary with the heating temperature, heating speed and oxidation medium (steam, water, furnace gas).
Read more: Seamless Steel Pipe Sizes













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.













