Square tubes (SHS
steel) and rectangular tubes
(RHS steel) are collectively referred to as Hollow
Structural Sections (HSS).
They are typically manufactured from
hot-rolled or cold-rolled strip steel through processes such as uncoiling,
flattening, rolling, welding, shaping, and cutting to length.
They can also be obtained through secondary
forming of hot-rolled seamless
steel pipes. Due to their different cross-sectional shapes, they differ
significantly in strength distribution, load-bearing capacity, applications,
and costs.
Square Tube Meaning
1. Material Structure of Square Tubes
Square tubes have a square cross-section
with four equilateral right angles.
Square tubes can be manufactured using
various processes such as hot rolling, cold rolling, cold drawing, or hot-dip
galvanizing, offering advantages such as low production costs and high
production efficiency.
3. Square Tube Sizes
Common sizes: 10×10mm,
20×20mm, 25×25mm, 40×40mm, 50×50mm, 100×100mm,
150×150mm
Wall thickness range: 0.6mm – 6.0mm
Length: Standard length 6m (customizable up
to 12m).
4. Load-Bearing Capacity of Square Tubes
Square tubes are superior in withstanding
bending loads and can withstand greater bending forces.
5. Applications of Square Tubes
Square tubes are widely used in petroleum,
chemical, power, and automotive industries, such as in automobile frames and
petrochemical oil pipelines.
Rectangular Tube Meaning
1. Material Structure of Rectangular Tubes
Rectangular tubes have a rectangular
cross-section with four right angles.
2. Manufacturing Process of Rectangular
Tubes
Rectangular tubes are generally
manufactured using hot rolling or cold rolling processes, resulting in
relatively high production costs.
Common sizes: 20×30mm,
25×50mm, 40×80mm, 50×100mm, 80×120mm, 100×200mm
Wall thickness range: 0.8mm – 8.0mm
Length: Standard 6m, custom lengths
available upon request.
4. Load-Bearing Capacity of Rectangular
Tubes
Rectangular tubes have higher strength than
square tubes for the same cross-sectional area.
5. Applications of Rectangular Tubes
Rectangular tubes are commonly used in
construction, machinery manufacturing, and other fields, such as steel frame
structures and corridor railings.
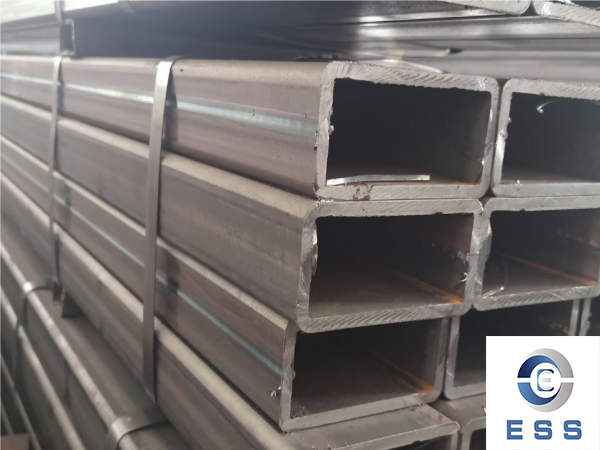
1. Choose Based on the Direction of Force
Choose square tubes (SHS steel):
When a structure needs to withstand
bending, torsion, or lateral forces from multiple directions (e.g., columns,
support frames, vehicle frames, machinery frames).
Square tubes, due to its symmetrical
cross-section, exhibits consistent strength in all directions, making it better
able to resist multi-directional stresses and torques.
Typical applications: automotive chassis,
towers, machinery frames, railings, equipment supports.
Choose rectangular tubes (RHS steel):
When the direction of force is clear (e.g.,
vertical compression or horizontal bending), rectangular tubes has stronger
bending resistance along its long side, allowing it to withstand greater loads
with the same material usage.
Typical applications: Building beams and
columns, portal frames, corridor structures, warehouse racking.
2. Selection Based on Structural Design and
Space Dimensions
Select square tubes (SHS steel):
When space is limited and a square and
symmetrical shape is required.
Square tubes has a compact cross-section,
suitable for columns, square frames, decorative structures, etc.
It also has a more harmonious appearance
and is often used in building facades, furniture, landscape railings, and other
applications requiring aesthetic appeal.
Select rectangular tubes (RHS steel):
For larger spans, material usage needs to
be optimized.
Rectangular tubes can more efficiently
distribute the moment of inertia of the material in the main force direction,
reducing weight and cost in beams, support arms, and frame beams.
3. Economic and Cost Considerations
Rectangular tubes offer superior structural
efficiency and lower costs. Square tubes offer advantages in symmetrical stress
distribution and aesthetic harmony.
4. Connection and Welding Requirements
Square tubes are easier to align during
welding, making them suitable for square nodes and symmetrical connection
structures.
Rectangular tubes require careful attention
to weld design and stress symmetry along their long and short sides during
connection.
For complex node stresses or situations
with limited weld space, square tubes are generally easier to install.
5. Quality Certification
When purchasing, ensure that the square
tubes meet relevant standards and quality certification requirements to
guarantee their reliability.
6. Price Comparison
In addition to the above factors, you
should compare the prices of square and rectangular tubes from different
suppliers or brands and make a final choice based on cost-effectiveness.

How to Identify Inferior Square Tube and
Rectangular Tubes?
1. Observe Creases and Ripples
High-quality tubes have a smooth surface,
while inferior products are prone to wrinkles or creases.
2. Check Weld Quality
Welds should be uniform and free of
porosity. Inferior pipes often exhibit weld cracks or incomplete penetration.
3. Touch and Gloss
High-quality pipes have a smooth surface
and a metallic luster; inferior pipes appear reddish or dull.
4. Measuring Wall Thickness
Use calipers to measure whether the wall
thickness matches the nominal thickness. Inferior products often misrepresent
their thickness.
5. Brand and Certification
Choose reputable manufacturers with ISO
certification and factory inspection reports.
FAQ
1. SHS Steel vs. RHS Steel: Which is Cheaper?
Prices may vary depending on:
Size and wall thickness
Steel grade and coating (galvanized or raw
steel)
Cutting and processing requirements
Generally, rectangular steel pipes (RHS)
may be slightly cheaper per meter, especially for larger spans, as it achieves
the required strength with less material. However, square steel pipes (SHS) are
generally more common in general-purpose construction.
2. Are Rectangular Tubes Recyclable?
Yes, rectangular tubes are recyclable.
It
is typically made of carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, all of which
are 100% recyclable and can be used to manufacture new metal products, making
it both environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.
Summary
In summary, when choosing between square
tubs (SHS) and rectangular tubs (RHS), the direction of force, load-bearing
requirements, appearance requirements, and cost factors should be considered
comprehensively: if multi-directional load-bearing performance and aesthetic
harmony are desired, choose square tubs; if high bending resistance and
material efficiency are desired, choose rectangular tubs.
Read more: SHS Steel vs. CHS Steel: Which is Stronger?













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.











