ERW Pipe Specifications and Models
ERW piping specifications and models are an essential part of many industrial systems and processes. They are made of steel and are critical components in the transport of fluids and gases. ERW pipe comes in a variety of sizes, shapes and materials, each with its own set of technical specifications. Knowing these specifications is critical to choosing the right pipe for the right job.
Types of ERW pipes
ERW pipe comes in many shapes and sizes. The most common type is round pipe, which is often used to transport liquids and gases in residential and commercial applications. Square and rectangular ducts are used in architectural applications as well as furniture and decorations. Special shaped tubing such as U-bends and can also be produced by ERW Tube Fabrication. ERW pipes are versatile and come in a variety of different sizes, shapes, models and specifications.
First, it is important to understand the
basic types of ERW pipes available in the market today. ERW pipe is generally
classified by its two main categories, including: straight welded pipe and spiral welded pipe.
1. Straight Seam Electric Resistance Welded
Pipe
Straight welded pipe is made by passing a
continuous strip of steel through sets of rollers that bend, shape and flatten
the strip before forming a welded joint along its length. This process creates
a seamless, leak-proof pipe with excellent mechanical properties.
Features: Uniform weld seam, smooth inner
and outer surfaces, and consistent wall thickness.
Typical Applications: Structural steel
pipe, water pipe, oil and gas pipeline, and automotive manufacturing.
2. Spiral Electric Resistance Welded Pipe
Spiral welded pipe, is made by rolling flat
metal strip into a tube shape and welding the edges together. This process
produces stronger, more reliable pipe with a higher pressure rating.
Features: Can produce larger diameter pipes
(>600mm) with improved pressure resistance.
Typical Applications: Large-scale oil and
gas transmission projects, submarine pipelines, and steel structure supports.

Material Specification
ERW pipe is typically made from mild steel
grades A53 to A106. The most commonly used grade is A53B, which has a minimum
yield strength of 30,000 psi. Other materials, such as stainless steel, copper,
and aluminum, can also be used to manufacture ERW pipe, depending on
application requirements.
|
Standard
|
Common Material
|
Minimum Yield Strength
|
|
ASTM A53 Grade B
|
Carbon Steel
|
≥ 240 MPa
|
|
ASTM A252 Grade 2 / 3
|
Carbon Steel
|
≥ 310 MPa
|
|
API 5L Grade B / X42 / X52
|
Pipeline Steel
|
≥ 245–360 MPa
|
|
EN 10219 S235 / S355
|
Structural Steel
|
≥ 235–355 MPa
|
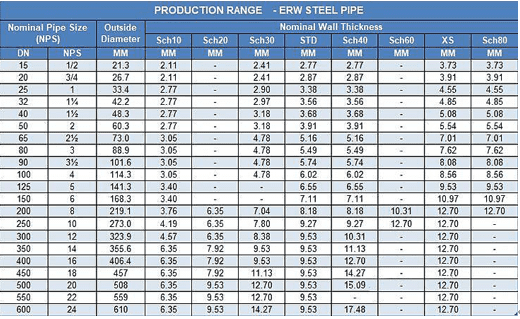
Dimensions
ERW pipe comes in a variety of sizes,
ranging from ½ inch to 16 inches. Each size has its own
technical specifications, including outer diameter, wall thickness, and
tolerances. Wall thickness must meet certain standards, such as ASTM A53, which
stipulates a maximum wall thickness of 12.5% of the
pipe's outer diameter. Tolerances for outer diameter and wall thickness vary by
manufacturer.
Form Factor
ERW pipe can be bent into a variety of
shapes depending on the application. Common shapes include round, square, and
rectangular. Other shapes, such as U-bends and swept elbows, can also be
created by adjusting the internal shape of the pipe. Bend specifications depend
on the material used and the required bend radius.
Round pipe: The most common, suitable for
fluid transport;
Square pipe: Used in building frames and
mechanical structures;
Rectangular pipe: Used in bridges and steel
structure supports;
Special shapes (U-bends, elbows, swept
elbows): Customizable to accommodate complex piping.
Weight Specification
ERW pipe is typically sold by weight, so it
is important to understand its weight specifications. Weight calculations
depend on the pipe's material composition, dimensions, and wall thickness. Pipe
with thicker walls is generally heavier than thinner, smaller walls.
The weight
of ERW pipe (per unit length) can be calculated using the following formula:
W = 0.02466 × (D − t) × t
Where:
W = Weight (kg/m)
D = Outside Diameter (mm)
t = Wall Thickness (mm)
For example, a 6" (DN150) Sch40 ERW
pipe has:
Outer Diameter 168.3mm, Wall Thickness
7.11mm → Weight approximately 22.85 kg/m
Parameters to Consider When Selecting
ERW Pipe
When selecting ERW pipe for a specific
application, certain parameters should be considered. These include Nominal
Pipe Size (NPS), Wall Thickness (WT), Material Grade, Coating Type, and
Hydrostatic Test Pressure.
1. Nominal Size and Wall Thickness
Nominal pipe size and wall thickness are
the two most important parameters when selecting ERW pipe, as they determine
the pipe's maximum capacity and pressure rating.
2. Materials and Coatings
The pipe material grade should be selected
based on the application and expected operating conditions. The coating type
should also be selected based on the pipe installation environment.
3. Inner Diameter
The inner diameter size of ERW pipe depends
on the number of times the pipe is rolled into a tubular shape and will affect
the overall strength and pressure rating of the pipe.
4. Hydrostatic Test Pressure
Manufacturers establish hydrostatic test
pressure specifications to ensure ERW pipe complies with relevant standards.
5. Other Variables
There are several other variables that
should be considered when specifying ERW piping. These include face type,
thread type and bore diameter.
The end face type can be from plain end to
beveled end or pipe
flange, and the thread type should be selected according to the
intended use of the pipe.
It is also important to consider the
pressure, temperature and chemical resistance of the pipe, as well as its load
carrying capacity.
Conclusion
ERW piping specifications and models are an essential part of many industrial systems and processes. Knowing the different types of plumbing available and their technical specifications is critical to choosing the right plumbing for the job. ERW piping comes in a variety of materials, sizes, shapes, and weights, and it is important to consider material, size, shape, weight, and design considerations when selecting piping.
Read more: The difference between erw and seamless black steel pipe













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.











