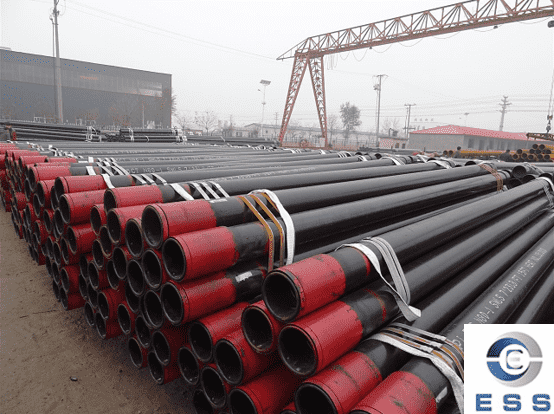
The oil and gas industry relies on durable
and high-performance materials to ensure safe and efficient operations. Among
these materials, carbon
steel pipes have become a fundamental material in the oil and gas
industry due to their high strength, pressure resistance, weldability, and
excellent cost advantages.
The oil and gas industry operates under
extreme conditions: high pressure, high temperature, corrosion, erosion, acidic
environments (H₂S), marine
environments, etc. Therefore, carbon steel pipes must meet stringent
international standards such as API, ASTM, and ASME.
Common Carbon Steel Pipe Standards for
Oil & Gas
1. API 5L Series
|
API 5L Level
|
Type
|
Grade Range
|
Typical Use
|
|
PSL1
|
Seamless/Welded
|
X42–X70
|
Conventional onshore pipelines
|
|
PSL2
|
Seamless/Welded
|
X52–X80+
|
Deep-sea, high-pressure,
sulfur-containing media pipelines (with stricter requirements for chemical
composition and impact toughness)
|
2. ASTM A53/A106
|
Standard
|
Type
|
Applications
|
|
ASTM A53
|
Seamless / ERW / Welded
|
Water, gas, steam, and low-pressure
transport and structural piping
|
|
ASTM A106(Gr.A/B/C)
|
Seamless
|
High-temperature, high-pressure fluids,
such as furnaces and boiler tubes in oil refineries
|
|
ASTM A333
|
Seamless
|
Cryogenic services, such as LNG equipment
|
|
ASTM A671 / A672
|
Welded
|
Pressure vessels, oil and gas pipelines
|
3. ASME B31.8
This standard applies to the design and
inspection of natural gas transmission and distribution systems and is one of
the important standards for pressure pipelines.
Why Does the Oil and Gas Industry Use
Carbon Steel Pipes
1. High Strength and Durability
Carbon steel pipes are renowned for their
excellent tensile strength. In deep oil and gas reservoirs with extremely high
pressures (up to 70–140 MPa), carbon steel pipes offer:
High yield strength (≥ 240–550 MPa);
Excellent resistance to internal pressure
bursts;
Good toughness and fatigue resistance.
2. Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to stainless steel or other
alloys, carbon steel pipes used in the oil and gas industry cost only 20–40% of their price without compromising performance. They meet most
oil and gas operating conditions, and corrosion resistance can be improved
through coatings. They are also easier to weld and install in the field.
3. Corrosion Resistance
With appropriate coatings and treatments,
carbon steel pipes can withstand harsh environments, including offshore
drilling and high-temperature applications.
4. Wide Range of Applications
Carbon steel pipes cover almost all oil and
gas industry scenarios:
Well control equipment;
Casing pipe and tubing (OCTG);
Onshore/subsea oil and gas pipelines;
Refinery equipment pipelines;
LNG, coal chemical, and petrochemical
engineering.
Common Types of Carbon Steel Pipes in
the Oil and Gas Industry
Ideal for high-pressure applications due to
their uniform structure.
Suitable for medium and low-pressure
systems, cost-effective.
3. Resistance Welded (ERW) Steel Pipes
Used for structural and low-pressure fluid
transport.
For the most demanding oil and gas
operations, seamless carbon steel pipes are often the first choice due to their
superior strength and leak-proof performance.
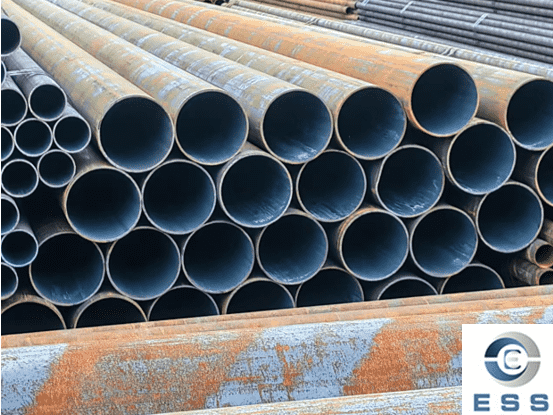

Applications of Carbon Steel Pipes in
Oil and Gas Extraction
1. Well Casing Pipe and Tubing
Carbon steel pipes are used to line the
wellbore, a process called casing construction, which prevents wellbore
collapse and protects groundwater from contamination. Tubing is used to
transport oil and gas to the surface.
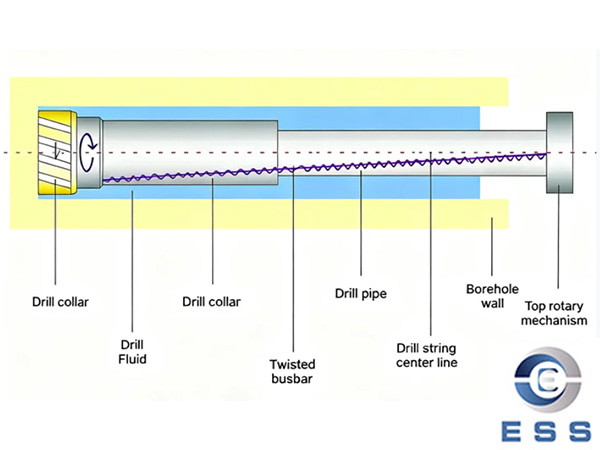
2. Directional Drilling
Modern deep wells and shale gas wells often
use horizontal or multi-branch directional drilling. Carbon steel pipes must
withstand: torsional, tensile, bending stress, continuous vibration, and
impact.
Applications of Carbon Steel Pipes in
Oil and Gas Transportation
1. Pipeline Networks
Extensive pipeline networks, sometimes
stretching thousands of miles, are constructed using carbon steel pipes. These
networks transport crude oil, natural gas, and refined petroleum products from
production sites to processing plants and distribution centers.
2. Subsea Pipelines
Transporting oil and gas from offshore
platforms to onshore facilities requires subsea pipelines.
Carbon steel pipelines are the material of
choice for these applications due to their ability to withstand high pressure
and corrosive marine environments.
3. Maintenance and Safety
Routine maintenance and integrity checks
are crucial for the safe operation of pipeline systems.
Carbon steel pipelines are known for their
durability, helping to reduce maintenance frequency and costs, thereby
improving overall operational safety.
Applications of Carbon Steel Pipes
in Oil and Gas Refining
1. Distillation Units
Crude oil is heated and separated into
various components in distillation units.
Carbon steel pipelines are responsible for
transporting these components smoothly through the various stages of refining
and maintaining their integrity under extreme conditions.
2. Hydrocracking and Catalytic Cracking
These refining processes break down large
hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more valuable molecules.
The high-pressure environments of these
units require the use of durable carbon steel pipelines.
3. Safety and Efficiency
The reliability of carbon steel pipes
ensures the smooth operation of the refining process, minimizing the risk of
leaks or malfunctions.
This improves safety and efficiency, which
are critical factors in refining operations.
How to Choose the Right Carbon Steel Pipe
When selecting carbon steel pipes for the oil and gas industry, the following factors should be considered:
Steel grade: e.g., API 5L, ASTM A106;
Wall thickness (Schedule): Sch 40, 80, 160, XS, XXS;
Corrosion resistance requirements: Whether FBE/3LPE internal and external coatings are required;
Operating pressure, temperature, and medium.
FAQ
1. What is the price of carbon steel pipe?
Price depends on: steel grade (X42–X80), wall thickness, diameter, whether it is seamless, whether it
is coated, and market raw material prices.
The carbon steel pipe price range is
generally USD 600–1200/ton (for reference only).
2. What is carbon steel pipe used for?
Carbon steel pipes are used for
transporting liquids, gases, and steam both above and below ground.
3. What are the sizes of carbon steel pipe?
Outer diameter: 1/2'' – 48'' (21.3 mm–1220 mm)
Wall thickness: Sch10–XXS
Length: 5.8m / 6m / 12m / SRL / DRL













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.