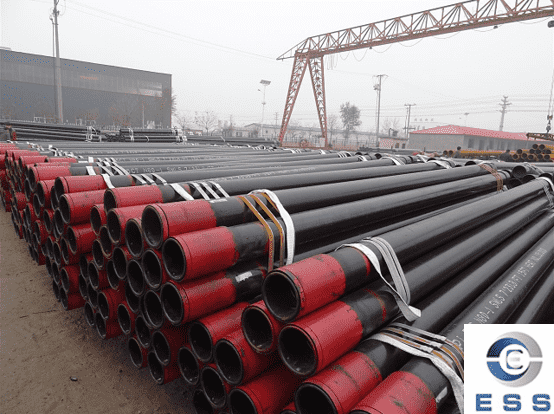
Technical requirements for welded pipes:
The technical requirements and inspection of straight seam welded pipes are based on the provisions of the GB3092 "Welded Steel Pipes for Low-Pressure Fluid Transmission". It can be delivered according to fixed length or double length. The surface of the steel pipe should be smooth, and defects such as folds, cracks, delamination, and lap welding are not allowed. The surface of the steel pipe is allowed to have minor defects such as scratches, scratches, weld misalignment, burns and scars that do not exceed the negative deviation of the wall thickness. The thickening of the wall thickness and the presence of inner seam weld bars are allowed at the weld. Welded steel pipes should be subjected to mechanical performance test, flattening test and flaring test, and must meet the requirements of the standard. The steel pipe should be able to withstand the internal pressure, carry out the 2.5Mpa pressure test every hour, and keep it without leakage for one minute. The method of eddy current flaw detection is allowed to replace the hydrostatic test.
The eddy current flaw detection is carried out according to the standard of GB7735 "Steel tube eddy current flaw detection inspection method". The eddy current flaw detection method is to fix the probe on the frame, keep a distance of 3~5mm between the flaw detection and the weld seam, and conduct a comprehensive scan of the weld seam by the rapid movement of the steel pipe. The flaw detection signal is automatically processed and sorted by the eddy current flaw detector. To achieve the purpose of flaw detection. The welded pipe after the flaw detection is cut off according to the specified length with a flying saw, and it is rolled off the assembly line through the turning frame. Both ends of the steel pipe should be chamfered with flat ends, printed with marks, and the finished pipes are packed in hexagonal bundles before leaving the factory.

Welded pipe processing method:
The welded pipe is a steel pipe whose weld seam is parallel to the longitudinal direction of the steel pipe. Generally, its strength is higher than that of the straight seam welded pipe. It can produce welded pipes with larger diameters with narrower billets, and welded pipes with different pipe diameters can also be produced with the same width of billets. But compared with the straight seam pipe of the same length, the weld length is increased by 30~100%, and the production speed is lower. So what are its processing methods?
1. Forging steel: a pressure processing method that uses the reciprocating impact force of the forging hammer or the pressure of the press to change the blank into the shape and size we need.
2. Extrusion: It is a processing method in which steel puts metal in a closed extrusion box, and one end applies pressure to make the metal extrude from the specified die hole to obtain a finished product with the same shape and size. It is mostly used for the production of non-ferrous metals material steel.
3. Rolling: A pressure processing method in which the steel metal billet passes through the gap between a pair of rotating rolls (various shapes), and the cross-section of the material is reduced and the length is increased due to the compression of the rolls.
4. Pulling steel: It is a processing method in which the rolled metal blank (type, pipe, product, etc.) is pulled through the die hole to reduce the cross section and increase the length. Most of them are used for cold processing.
Pre-welding of welded pipes:
Pre-welding includes joints and welds.
1. The joint (that is, the forming seam) has no misalignment or the misalignment is less than the specified value. Generally, the amount of misalignment is ≤ 8% of the plate thickness, and the maximum is not more than 1.5mm.
2. It is necessary to ensure that the weld seam has a suitable penetration depth and deposition amount. It is necessary to ensure that there is no cracking or burn-through after welding, and it is also necessary to control the height of the weld seam so that the reinforcement of the external weld seam will not be affected.
3. The weld bead is continuous and formed to facilitate the external welding after guarantee.
4. There are no defects such as welding deviation, porosity, cracks, slag inclusions, burn-through and back welding bumps in the weld seam, and the center deviation of the weld seam is required to be ≤1mm.
5. No arc burn, little splash, no influence on pipe end bevel and surface.
6. The weld seam matches the base metal, and the physical and chemical properties of the weld metal meet the requirements.
The essentials of welded pipe welding:
The forming methods for manufacturing large-diameter longitudinally welded pipes include UOE forming, row-roll forming (CFE), CE forming, etc. For the last process of most forming methods, the full-length diameter expansion of the welded tube blank is performed again to improve the shape of the welded steel tube. Diameter expansion has become an important process to ensure the finished pipe in the production of large diameter longitudinal welded pipe. Diameter expansion is a pressure processing process that uses hydraulic or mechanical means to apply force from the inner wall of the steel pipe to expand the steel pipe radially outward.
Compared with the hydraulic method, the mechanical method has simpler equipment and higher efficiency. It has been adopted in several large-diameter straight seam welded pipe pipeline expansion processes in the world. The mechanical expansion uses the split fan-shaped block at the end of the expansion machine to expand radially. , the process of making the tube blank along the length direction in a stepwise manner to realize the plastic deformation of the full tube length in sections.
1. Initial full circle stage. The fan-shaped blocks are opened until all the fan-shaped blocks touch the inner wall of the steel pipe. At this time, the radii of all points in the inner circular pipe of the steel pipe within the step range are almost the same, and the steel pipe obtains a preliminary full circle.
2. Nominal inner diameter stage. The fan-shaped block starts to reduce the moving speed from the front position until it reaches the required position, which is the required position of the inner circumference of the finished tube.
3. Springback compensation stage. The fan-shaped block starts to lower the speed at the position of the second stage until it reaches the required position, which is the position of the inner circumference of the steel pipe before springback required by the process design.
Seamless vs welded pipe
1. In terms of appearance, the difference between seamless steel pipes and welded steel pipes is that there are welding ribs on the inner wall of the welded pipes, while the seamless ones do not.
2. The pressure of the seamless steel pipe is higher, and the welded pipe is generally about 10 MPa. Now the welded pipe is made to be seamless.
3. The seamless steel pipe is formed at one time during rolling. Welded steel pipes need to be rolled and welded, usually with spiral welding and direct welding. The performance of the seamless pipe is better, and of course the price is also higher.













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.