What Is API 5DP Drill Pipe
API 5DP drill pipe is a type of OCTG pipe, a
threaded pipe at the rear end used to connect surface drilling equipment to the
mill or bottom-hole assembly at the bottom of the drilling rig.
Its purpose is to transport drilling mud to
the drill bit and to coordinate with the drill bit to raise, lower, or rotate
the bottom-hole assembly. Drill pipe must be able to withstand significant
external pressure, twisting, bending, and vibration.
In oil and gas exploration and mineral
production, API 5DP drill pipe can be reused multiple times and is an
indispensable component in drilling operations.
For example, S135 requires a yield strength
of ≥135 ksi (approximately 931 MPa), making it suitable
for ultra-deep well operations.
API 5DP Drill Pipe Size Range
1. Size Range
2
3/8" to 5 1/2" (60.3 mm to 139.7 mm).
2. Thickness Range
6.5 mm to 12.7 mm
3. Length
R1, R2, R3.
Ranger 1 (R1) is the shortest length and is
more commonly used to size production tubing or casing pipe,
ranging from 18 to 22 feet.
Ranger 2 (R2) is considered the standard
length for drill pipe and ranges from 27 to 31 feet.
Ranger 3 (R3) is common in casing and is
also used in deepwater drilling applications. The increased length reduces the
number of tool joints per drill pipe.
API 5DP Drill Pipe Steel Grade
API 5DP is designed specifically for drill
pipe and specifies material grades such as E75, X95, G105, and S135 (the number
represents the minimum yield strength in ksi). The differences are primarily in
yield strength, tensile strength, and toughness:
1. E75
Yield strength ≥ 75
ksi (517 MPa) and is primarily used in shallow or conventional wells.
2. X95
Yield strength ≥ 95
ksi (655 MPa), suitable for medium-deep well operations.
3. G105
Yield strength ≥ 105 ksi (724 MPa), suitable for deep wells and high-intensity operating
environments.
4. S135
Yield strength ≥ 135 ksi (931 MPa), suitable for ultra-deep wells, high-pressure wells, and
complex formations.
API 5DP Drill Pipe Mechanical Properties
Mechanical property requirements for
different API 5DP drill pipe grades:
|
Pipe body
|
Grade
|
Yield strength
Min
|
Yield strength
Max
|
Tensile strength
Min
|
Elongation
|
Charpy impact
|
|
E75
|
75000 Psi / 517 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 724 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 689 MPa
|
625000A0 .2/U0.9
|
Average 80 J
Single 65 J
|
|
X95
|
95000 Psi / 655 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 862 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 724 MPa
|
Average 80 J
Single 65 J
|
|
G105
|
1E+05 Psi / 724 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 931 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 793 MPa
|
Average 80 J
Single 65 J
|
|
S135
|
1E+05 Psi / 931 MPa
|
2E+05 Psi / 1138 MPa
|
1E+05 Psi / 1000 MPa
|
Average 80 J
Single 65 J
|
|
Weld
zone
|
Tool joint
|
1E+05 Psi / 827.4 MPa
|
-
|
1E+05 Psi / 965.3 MPa
|
≥13%
|
HBW ≥285
Average 80 J
Single 65 J
|
|
E75
|
75000 Psi / 517 MPa
|
-
|
1E+05 Psi / 689 MPa
|
Average 40 J
Single 27 J
|
|
X95
|
88000 Psi / 609 MPa
|
-
|
1E+05 Psi / 712 MPa
|
Average 40 J
Single 27 J
|
|
G105
|
95000 Psi / 655 MPa
|
-
|
1E+05 Psi / 724 MPa
|
Average 40 J
Single 27 J
|
|
S135
|
1E+05 Psi / 724 MPa
|
-
|
1E+05 Psi
|
Average 40 J
Single 27 J
|
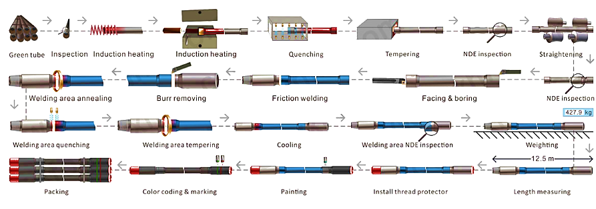
API 5DP Drill Pipe Manufacturing Process
Drill pipe is manufactured in strict
accordance with the API 5DP standard. Drill pipe manufacturing is a strictly
controlled process designed to ensure that the final product meets the
stringent standards required for drilling operations.
API 5DP Drill Pipe Manufacturing Process
Material selection → Pipe forming → Heat treatment → Quenching and tempering → End upset → Tool joint welding → Inspection and testing → Marking and coating.
API Specification 5DP Drill Pipe Types
1. Standard Drill Pipe
The most common type of drill pipe.
Used for conventional drilling in onshore
and offshore environments.
HWDP is thicker and heavier than standard
drill pipe, designed to increase the weight of the drill string, reduce
buckling, and improve stability.
Used for directional drilling and extended
reach wells.
3. Auger Drill Pipe
Auger drill pipe features spiral grooves to
reduce friction and wear during drilling. Used in operations where friction
reduction is critical.
4. Square Drill Pipe
Square drill pipe is less common and
features a square cross-section, providing increased rigidity. Used in specific
drilling scenarios requiring a rigid drill string.
5. Hexagonal Drill Pipe
Hexagonal drill pipe has a hexagonal
cross-section for increased torsional strength. Used in high-torque drilling
operations.
API 5DP Drill Pipe Threads
The connections between drill pipe sections
are critical to maintaining the integrity of the drill string. API 5DP drill
pipe has several connection types:
1. Internal Flush (IF) Threads
This flush internal profile design reduces
pressure drop and turbulence, making it suitable for high-pressure wells.
2. Full Hole (FH) Threads
This connection features a larger bore
diameter and larger fluid passages, making it suitable for deep wells and
high-flow mud transport.
3. API Conventional (API REG) Threads
This connection offers a wide range of
applications and is robust and durable. It is commonly used in standard
drilling operations.
4. Numerical Connection (NC)
This high-torque design is commonly used in
deep wells, hard formations, and complex drilling conditions.
Differences between API 5D and API 5DP Drill
Pipe
Both API 5D and API 5DP are drill pipe
standards developed by the American Petroleum Institute (API). To address the
shortcomings of API 5D and provide a comprehensive specification covering the
entire drill pipe lifecycle, API released API 5DP to replace API 5D.
Simply put, the core differences between
them are:
1. API 5D
An earlier standard that only regulates the
drill pipe body (raw material), primarily controlling dimensions, chemical
composition, and basic mechanical properties.
2. API 5DP
An upgraded standard that covers the entire
finished drill pipe product, including the pipe body, welds, joints, and final
inspection requirements, more closely resonating with actual operating
conditions.
Summary
API 5DP drill pipe is an indispensable and
critical tool in oil and gas drilling. Its strict material grades, dimensional
standards, mechanical property requirements, as well as standardized
manufacturing processes and joint designs, ensure safe and efficient drilling
operations.
Read more: API 5DP Drill Pipe Specs & Sizes or Guide To Drill Pipe Steel Grades













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.