A Comprehensive Comparison of Seamless vs Welded Pipes
Pipes are used for the transportation of fluids, gases, and sometimes solids from one point to another. Pipes are essential components of many industries, including oil and gas, water and sewage, chemical processing, and power generation. Pipes come in different forms, sizes, and materials, with the two primary types being seamless and welded pipes. The choice of the type of pipe to use in a particular application depends on several factors, including the intended use, the operating conditions, the cost, and the material availability. This essay provides a comprehensive comparison of seamless and welded pipes, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, applications, and manufacturing processes.
What are seamless pipes?
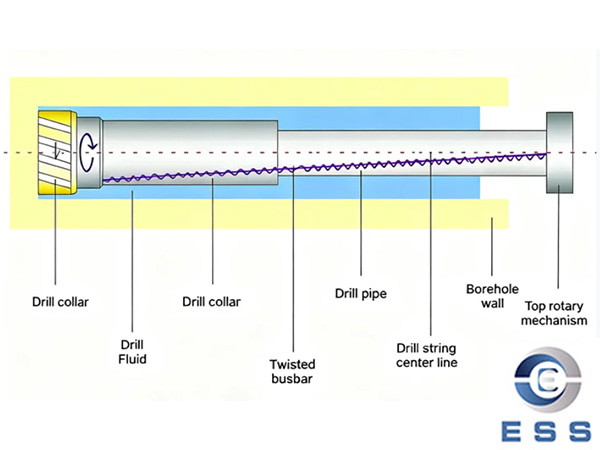
Seamless pipes are pipes that are produced without any welding or joining process. Seamless pipes are made from solid cylindrical billets, which are heated and then stretched over a mandrel to form the desired shape and size. Seamless pipes have a uniform structure, with no welded joints or seams that could be potential weak points. Seamless pipes are produced using two primary methods: hot-rolling and cold-drawing.

Hot-rolling method
The hot-rolling method is used to produce seamless pipes from large cylindrical billets. The billet is heated to a high temperature, typically above 1200°C, and then passed through a series of rollers that gradually reduce the diameter of the billet. The hot-rolling method is used to produce pipes with diameters ranging from 21.3 mm to 660 mm and wall thicknesses ranging from 2.3 mm to 60 mm. The hot-rolling method is relatively inexpensive compared to the cold-drawing method, and it produces pipes with a rough surface finish.
Cold-drawing method
The cold-drawing method is used to produce seamless pipes with a higher degree of precision and a smoother surface finish than pipes produced using the hot-rolling method. The cold-drawing method involves pulling a hot-rolled or extruded billet through a series of dies to reduce its diameter and increase its length. The cold-drawing method is used to produce pipes with diameters ranging from 6 mm to 250 mm and wall thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to 20 mm. The cold-drawing method produces pipes with a smooth surface finish and a high degree of dimensional accuracy.
Advantages of seamless pipes
1、Strength and durability
Seamless pipes have a uniform structure, with no welded joints or seams that could be potential weak points. Seamless pipes are therefore stronger and more durable than welded pipes, making them ideal for high-pressure applications.
2、Corrosion resistance
Seamless pipes are made from high-quality materials, such as stainless steel, which are resistant to corrosion. Seamless pipes are therefore ideal for use in corrosive environments, such as chemical processing plants, offshore oil rigs, and marine applications.
3、Precision
Seamless pipes are produced using a high degree of precision, with a smooth surface finish and a high degree of dimensional accuracy. Seamless pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications where precise measurements are required, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
4、Reduced leakage
Seamless pipes have no welded joints or seams, reducing the risk of leakage. Seamless pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications where leakage could be dangerous or costly, such as in the oil and gas industry.
5、Lower maintenance costs
Seamless pipes require less maintenance than welded pipes, as they have no welded joints or seams that could be potential weak points. Seamless pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications where maintenance costs need to be kept low, such as in the water and sewage industry.
Disadvantages of seamless pipes
1、Higher cost
Seamless pipes are more expensive than welded pipes, as they require a more complex manufacturing process. Seamless pipes are
therefore not always the most cost-effective option, especially for applications that do not require the higher strength or corrosion resistance of seamless pipes.
2、Limited size range
Seamless pipes have a limited size range compared to welded pipes. The maximum diameter of seamless pipes is typically around 660 mm, while welded pipes can be produced in much larger diameters.
3、Manufacturing limitations
The manufacturing process for seamless pipes can be limited by the availability of materials and the production capabilities of the manufacturer. Some materials, such as titanium and high-alloy steels, are difficult to work with and may not be available in seamless form.
What are welded pipes?
Welded pipes are pipes that are produced by welding two or more pieces of metal together. Welded pipes can be produced using various welding methods, including electric resistance welding (ERW), submerged arc welding (SAW), and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). Welded pipes can be produced in a range of sizes and materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and high-alloy steels.

Electric resistance welding (ERW)
Electric resistance welding (ERW) is a welding method that uses a combination of heat and pressure to weld two or more pieces of metal together. ERW is used to produce pipes with diameters ranging from 21.3 mm to 660 mm and wall thicknesses ranging from 2.3 mm to 22 mm. ERW is a cost-effective method of producing welded pipes, and it produces pipes with a smooth surface finish.
Submerged arc welding (SAW)
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a welding method that uses a granular flux to protect the weld from contamination. SAW is used to produce pipes with diameters ranging from 16 mm to 1500 mm and wall thicknesses ranging from 3 mm to 65 mm. SAW is a cost-effective method of producing welded pipes, and it produces pipes with a smooth surface finish.
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW)
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) is a welding method that uses a tungsten electrode to produce an electric arc that melts the metal. GTAW is used to produce pipes with diameters ranging from 3 mm to 300 mm and wall thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to 10 mm. GTAW is a precise method of producing welded pipes, and it produces pipes with a smooth surface finish.
Advantages of welded pipes
1、Cost-effective
Welded pipes are generally less expensive than seamless pipes, as the manufacturing process is less complex and requires less material. Welded pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications where cost is a primary consideration, such as in the water and sewage industry.
2、Large size range
Welded pipes can be produced in a wide range of sizes, including large diameters. Welded pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications that require large-diameter pipes, such as in the oil and gas industry.
3、Flexibility
Welded pipes can be produced using a variety of welding methods and materials, making them highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
4、Easy to manufacture
Welded pipes are relatively easy to manufacture, and the manufacturing process can be automated for high-volume production. Welded pipes are therefore ideal for use in applications where large quantities of pipes are required, such as in the construction industry.
Disadvantages of welded pipes
1、Weaker than seamless pipes
Welded pipes have welded joints or seams that can be potential weak points. Welded pipes are therefore weaker than seamless pipes and may not be suitable for use in high-pressure applications.
2、Limited corrosion resistance
Welded pipes may be more prone to corrosion than seamless pipes, especially at the welded joints or seams. This is because the welding process can alter the material properties and reduce its resistance to corrosion.
3、Surface finish
Welded pipes may have a rougher surface finish compared to seamless pipes. This can make welded pipes more difficult to clean and maintain, especially in applications where hygiene is important.
4、Quality control
The quality of welded pipes depends on the welding process and the skills of the welder. Poor welding can result in defects such as cracks and porosity, which can weaken the pipe and compromise its integrity.
Applications of seamless pipes
Seamless pipes are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1、Oil and gas industry
Seamless pipes are commonly used in the oil and gas industry for transporting fluids under high pressure and temperature. They are used for drilling, extraction, and transportation of crude oil and natural gas.
2、Power generation
Seamless pipes are used in the power generation industry for transporting steam and other fluids under high temperature and pressure. They are used in boilers, steam turbines, and other power generation equipment.
3、Chemical and petrochemical industry
Seamless pipes are used in the chemical and petrochemical industry for transporting corrosive and hazardous fluids. They are used for manufacturing chemicals, fertilizers, and other petrochemical products.
4、Automotive industry
Seamless pipes are used in the automotive industry for manufacturing engine components and exhaust systems. They are used for improving the performance and efficiency of vehicles.
Applications of welded pipes
Welded pipes are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1、Water and sewage industry
Welded pipes are commonly used in the water and sewage industry for transporting water and sewage under low to medium pressure. They are used for water supply, drainage, and sewage treatment.
2、Construction industry
Welded pipes are used in the construction industry for structural applications such as building frames, bridges, and tunnels. They are used for their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
3、Mining industry
Welded pipes are used in the mining industry for transporting minerals and ores from mines to processing plants. They are used for their strength and durability in harsh environments.
4、HVAC industry
Welded pipes are used in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) industry for transporting fluids such as water, refrigerants, and air. They are used for their strength and durability in harsh environments.
Conclusion
Seamless and welded pipes have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application. Seamless pipes are generally stronger and more corrosion-resistant than welded pipes, but they are also more expensive and have a limited size range. Welded pipes are generally less expensive and can be produced in a wide range of sizes, but they may be weaker and more prone to corrosion than seamless pipes.
When choosing between seamless and welded pipes, it is important to consider factors such as the pressure and temperature of the fluids being transported, the size and diameter of the pipes, and the overall cost of the project. Consulting with a qualified engineer or pipe supplier can help ensure that the right type of pipe is selected for the specific application, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Read more: The Benefits and Drawbacks of Seamless vs Welded Pipes













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.