Cold-rolled seamless steel pipes, with
their high dimensional accuracy, excellent surface quality, outstanding
mechanical properties (especially strength), and unique ability to produce
small-diameter, thin-walled tubes, have become the preferred material for
high-end applications with stringent requirements for precision, performance,
and reliability.
This article will provide a detailed
introduction to the production, specifications, materials, standards, and
purchasing guidelines for cold-rolled pipes and cold-rolled seamless steel
pipes.
Seamless steel pipes are pipelines
with a hollow section and are used in large quantities for conveying fluids,
such as pipelines for conveying oil, natural gas, gas, water and certain solid
materials. Compared with solid steel such as round steel, steel pipe has a lighter
weight when the bending and torsion strength is the same. It is a kind of
economical cross-section steel and is widely used in pipeline engineering.
Seamless Steel Pipe Production Types
The production process of general seamless
steel pipes can be divided into two types: cold-rolled and hot-rolled.
In appearance, cold-rolled seamless steel
pipes are shorter than hot-rolled seamless steel pipes.
The wall thickness of cold-rolled seamless
steel pipes is generally higher than that of hot-rolled seamless steel pipes.
But the surface looks brighter than
thick-walled seamless steel pipes. There is not much roughness on the surface,
and there are not too many burrs on the caliber.
The maximum nominal diameter of cold rolled
pipe is 200 mm, and the maximum nominal diameter of hot rolled pipe is 600 mm.
Classification of Cold Rolled Pipes
Cold rolled pipes can be further classified into several types based on their material, manufacturing process, and application. Here are some common classifications:
1. Classification by Material
Carbon Cold Rolled Pipes: Steel tubes made from carbon steel through a cold-rolling process, possessing excellent mechanical and processing properties.
Alloy Cold Rolled Pipes: Made by adding alloying elements to carbon steel to improve its corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, or wear resistance, among other special properties.
Stainless Steel Cold Rolled Pipes: Made from stainless steel, possessing excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
2. Classification by Manufacturing Process
Ordinary Cold Rolled Pipes: Steel pipes manufactured using conventional cold-rolling processes, suitable for general applications.
Precision Cold Rolled Pipes: Manufactured using more precise cold-rolling equipment and processes, possessing higher dimensional accuracy and surface finish, suitable for applications requiring high precision.
3. Classification by Application
Cold Rolled Pipes for Machinery: Primarily used in manufacturing mechanical parts, transmission components, etc., requiring high strength and rigidity.
Cold Rolled Pipes for Fluid Transportation: Used for transporting fluids such as water, oil, and gas, requiring good sealing and corrosion resistance.
Cold Rolled Pipes for Structural Applications: Used as supporting components in building structures, bridges, ships, etc., requiring high load-bearing capacity and stability.
Cold Rolled Pipe Pros and Cons
1. Advantages
The main advantage of cold rolled pipe is
the large reduction rate of section, especially the strong wall reduction
ability.
For carbon steel, the reduction rate of
cross-section in one rolling can reach 80%~83%, and for
alloy steel it can reach 72%~75%.
2. Disadvantage
The main disadvantage is the difficulty of
tool replacement. The cold rolling method is often used in combination with the
cold drawing method to produce cold-drawn billets, in addition to being
directly used to produce some of the cold-rolled pipes with higher precision.
This can not only give full play to the
wall reduction ability of cold rolling, but also cleverly use the advantages of
easy replacement of cold drawn tools, which is conducive to improving
productivity, expanding product production range and improving the surface
quality of steel pipes.
Cold Rolled Pipe Production
At present, the production of cold-rolled
pipes mostly uses periodic cold-rolled pipe mills. The working feature of the
periodic cold rolling pipe mill is that the steel pipe and the mandrel do not
move, and the reciprocating motion of the rack drives the reciprocating rolling
steel pipe, and uses variable-section-shaped compression rolling parts to
achieve the purpose of diameter reduction and wall reduction.
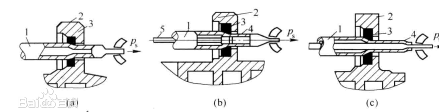
When the mill and roll are at the original
position a, the pass size is the largest (slightly larger than the outer
diameter of the blank); when the stroke limit position b is reached, the pass
is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the finished product; before the
position b is reached. The smallest is equal to the outer diameter of the
finished product.
At the original position a, the pipe
material is fed in, depending on the size of the rolling mill, each feeding is
3-30mm. At position b, the tube material is turned over 60°~90° each time, so that the pipe wall can be smoothed when the roller
returns.
After returning to the original position a,
feed the tube material to start the next cycle of rolling. The pipe material is
rolled repeatedly in this way, and finally the cold-rolled steel pipe of the
required size is rolled.
Cold Rolled Pipe Specification
The specification range of cold rolled
steel pipe is: outer diameter 4.0~450mm; wall thickness
0.04~60mm.
Compared with the cold drawing method, the
periodic cold rolled pipe method has the advantages of large pass area
shrinkage, no difficulty, and high yield: the disadvantage is that the
production speed is slow, the tool cost is expensive, and the intermediate
processing cost is just high.
Cold Rolled Seamless Steel Pipe
Cold rolled seamless steel pipe is a
seamless steel pipe rolled below its recrystallization temperature. During cold
rolling, steel is rolled at room temperature to form a seamless steel pipe of
the required shape and size. Because no phase transformation occurs during cold
rolling, its dimensional accuracy and surface finish are high.
1. Characteristics
Cold rolled seamless steel pipe has a
bright surface, high dimensional accuracy, and uniform wall thickness.
Due to the greater deformation resistance
of steel during cold rolling, the production cost of cold rolled seamless steel
pipe is higher, and its price is also relatively high.
Cold rolled seamless steel pipe is suitable
for applications requiring high dimensional accuracy and surface finish, such
as precision instruments, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems.
2. Applications
Machinery Manufacturing: As a raw material
for mechanical parts, such as shafts, sleeves, and bearings.
Hydraulic Equipment: Used to manufacture
hydraulic components and piping systems requiring high dimensional accuracy and
surface finish.
Structural Support: Due to its high
strength and good plasticity, it is often used as a supporting material for
various structures, such as bridges, buildings, and towers.

Production Steps of Cold Rolled Seamless
Steel Pipes
The production process of cold-rolled
seamless steel pipes mainly includes the following steps:
1. Billet Preparation
Select high-quality steel as raw material,
and perform cutting, rust removal, and other treatments to ensure the quality
and cleanliness of the raw materials.
2. Pickling and Lubrication
Pickle the billet to remove surface oxides
and dirt, and apply lubricant to reduce friction during rolling.
3. Cold Rolling
Continuously roll or cold draw the treated
steel using a cold rolling mill to form a seamless steel pipe. Strict control
of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and rolling speed is required
during this process to ensure the quality and precision of the steel pipe.
4. Heat Treatment
The formed steel pipe needs to undergo heat
treatment, such as annealing, to improve its mechanical properties and
corrosion resistance.
5. Straightening and Finishing
Straighten the heat-treated steel pipe to
eliminate defects such as bending and twisting, and perform finishing
processing to improve surface smoothness.
6. Inspection
The processed steel pipes undergo quality
inspection, including visual inspection, dimensional measurement, and
non-destructive testing, to ensure they meet relevant standards and
requirements.
Common Materials for Cold Rolled
Seamless Steel Pipes
Carbon structural steel (e.g., 10#, 20#,
45#)
Alloy structural steel (e.g., 20Cr, 40Cr,
20CrMo, 30CrMnSiA, 42CrMo)
Bearing steel (e.g., GCr15)
Stainless steel (Austenitic stainless steel
such as 304, 316L; Martensitic stainless steel such as 420; Ferritic stainless
steel such as 430, etc.)
Tool steel
Special alloys (e.g., Nickel-based alloys,
Titanium alloys, etc.)
Standards for Cold Rolled Seamless Steel
Pipes
1. Chinese National Standards (GB/T): such
as GB/T 3639 "Cold-Drawn or Cold-Rolled Precision Seamless Steel Pipes",
GB/T 8713 "Precision Inner Diameter Seamless Steel Pipes for Hydraulic and
Pneumatic Cylinders", etc.
2. International Standards (ISO): Such as
ISO 3304, ISO 3305, ISO 3306, etc., standards for precision seamless pipes.
3. German Industrial Standards (DIN): Such
as DIN 2391,
DIN 2393, etc.
4. American Society for Testing and
Materials (ASTM): Standards such as ASTM A519 (Seamless carbon and alloy steel
tubes for machine applications) and ASTM A269 (Seamless and welded austenitic
stainless steel tubes for general purposes) also include specifications for
cold-rolled products.
5. Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS):
Standards such as JIS G 3445 (Carbon
steel pipes for mechanical structures) and JIS G 3463 (Angle tubes for
general structural purposes) also cover requirements for cold-rolled precision
tubes.
6. Specialized Standards: Many downstream
industries (such as automotive, hydraulics, and bearings) have their own more
stringent enterprise or industry standards.
Specifications of Cold Rolled Seamless
Steel Pipes
The specifications of cold rolled seamless
steel pipes are generally marked according to their outer diameter and wall
thickness.
Common outer diameters include φ6mm, φ8mm, φ10mm, φ12mm, φ14mm, φ16mm, φ18mm, and φ20mm.
Wall thicknesses are generally 0.5mm,
0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.5mm, 2.0mm, 2.5mm, and 3.0mm.
Custom thicknesses can also be made
according to customer requirements.
Mechanical Properties of Cold Rolled
Seamless Steel Pipes
The mechanical properties of cold rolled
seamless steel pipes include tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation.
Generally, tensile strength is required to
be above 400MPa, yield strength above 240MPa, and elongation above 15%. These
properties ensure the durability and safety of the pipe during use.
Procurement Guide
1. Don't Just Look at the Price
Many people choose hot-rolled pipes because
they're cheaper, but if high-precision applications are needed, this can
increase subsequent processing costs, making it a poor investment. Conversely,
choosing cold-rolled pipes for ordinary infrastructure applications is a waste
of money.
2. Check the Test Report
Request material certificates and test
reports from cold rolled steel pipe suppliers or manufacturers to confirm that
the steel pipe's chemical composition (such as carbon content and alloy element
content) and mechanical properties (tensile strength and yield strength) meet
the requirements.
3. Check the Surface Quality
Oxide scale is normal on the surface of hot
rolled pipes, but obvious cracks or dents indicate a defective product. For
cold rolled pipes, scratches or pitting on the surface indicate substandard
processing; do not purchase them.
Summary
Cold rolled seamless steel pipes, with
their high dimensional accuracy, excellent surface quality, outstanding
mechanical properties (especially strength), and unique ability to produce
small-diameter, thin-walled pipes, have become the preferred material for
high-end applications with stringent requirements for precision, performance,
and reliability.
Read more: The difference between cold drawn pipe and cold rolled pipe or Production process of seamless steel pipe













 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.











